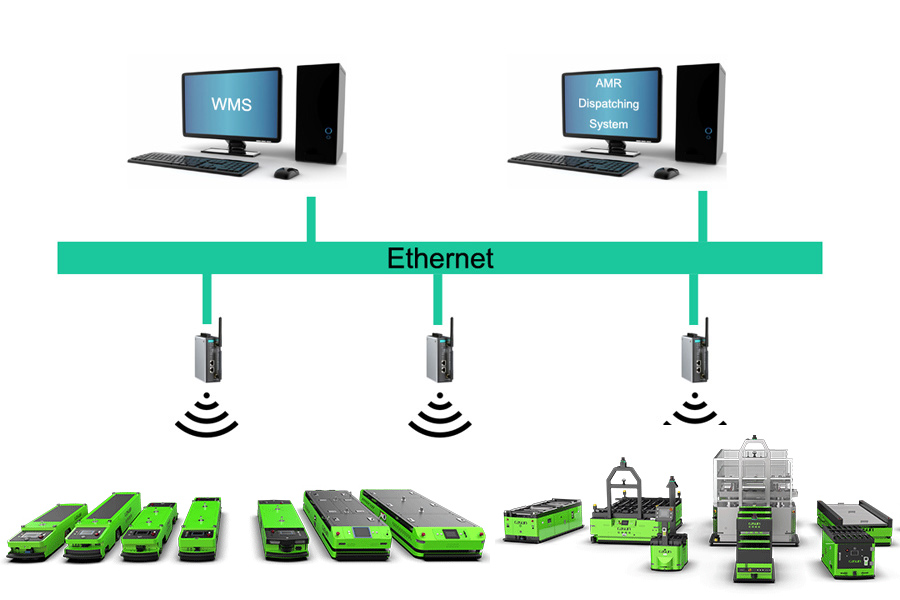
With the gradual development of science and technology, we are increasingly demanding the degree of intelligent automation in the industrial production process.
Then in this issue, Let’s analyze the various charging methods of the AGV together!
Contents
- First, according to the charging time can be divided into random charging and full-cycle charging
- Second, the charging area can be divided into online charging and offline charging
- Third, according to the operation method classification into manual mode, battery replacement mode, automatic charging
- Fourth, according to the electrical connection method of the charger can be divided into contact and wireless charging
- How to extend the battery life of AGV & AMR
First, according to the charging time can be divided into random charging and full-cycle charging
1 random charge
It means that the parking stations of the AGV can be charged at any time without any time limit. If there are more charging points, it can ensure that the loss of the AGV during the working process can be replenished in time, so as to achieve shallow charging of the battery, prolong the service life of the battery and reduce the required battery capacity.
2 full cycle charging
It means that the AGV is required to be charged after the service is taken out of the service, and the charging is performed when the charge of the battery falls within the specified range.
Of course, there are currently charging modes that are combined in the above two ways.
Second, the charging area can be divided into online charging and offline charging
1 online charging
It means that the AGV does not need to leave the working line and does not need to be charged for a specific time. It is only necessary to use a short time in the working process to perform the charging mode. Reasonable use of the fragmentation time of the AGV does not take up its working time. This method is also an extension of random charging. Embed the charging station into the workflow of the AGV trolley to further improve the efficiency of the AGV trolley.
2 offline charging
It means that after the AGV exits the service, it will enter the charging area or a special charging station for charging mode.
Third, according to the operation method classification into manual mode, battery replacement mode, automatic charging
When the power of the AGV is insufficient, the ground control center will direct the AGV to the designated charging area. The corresponding professional personnel manually complete the electrical connection between the AGV and the charger to perform charging. After the charging is completed, the working state of the is also manually restored.
The manual charging mode of the AGV is very reliable and easy to implement and low in equipment cost. It is usually used in the standard work system where the degree of automation is not particularly high and the number of vehicles is small. In order to ensure the endurance of the AGV, it is necessary to equip the battery with a large capacity. Therefore, continuous operation of the 24-hour AGV trolley cannot be achieved.
The replacement battery charging is when the power of the AGV is insufficient, the corresponding professional personnel manually replace the battery pack, and the AGV is put into use. The replaced battery will be used after charging. Its main features are simple, fast, and can achieve 24-hour continuous work of the AGV trolley throughout the day. However, it takes twice as many battery packs as it is costly and primitive. Usually used to respond to work timeliness is also very high requirements, but the above two methods are required to take care of, not only waste of manpower and automation will be reduced. Once the charge is lost, the AGV will not work.
Automatic charging is the automatic reporting and request charging when the AGV needs supplementary power. It is commanded by the ground control center and drives to the designated charging area. The charging connector of the vehicle and the charging system of the ground is automatically connected to implement charging. When the charging is completed, the AGV will automatically leave the charging system and then drive to the work area for normal work. This type of AGV trolley is suitable for applications where the number of vehicles is small, the work cycle is long and the degree of automation is high.
Fourth, according to the electrical connection method of the charger can be divided into contact and wireless charging
Contact charging is a charging circuit that requires charging contacts and cables to connect the vehicle to the power supply system. The contact charging mode provides a large charging current for fast charging. This is also a way for everyone to choose more. However, this method cannot be applied to frequent random charging, and there is wear of the charging contacts, so regular replacement is required. Moreover, fire may occur during the charging process, so there will be a case for all. In addition, since the charging contact is an exposed component, it cannot work normally in a humid, low-temperature condensation, flammable, or explosive environment.
Wireless charging refers to a non-contact charging device. It is not necessary to use a cable. It is only necessary to connect the vehicle to the power supply system, discard the charging contacts, and the electrical device and the charger can be exposed without conductive contacts.
The wireless charging technology electrically isolates the charging end from the energy storage system of the AGV and fundamentally eliminates the drawbacks caused by the in-line charging method. Therefore, it is more complete and more applicable.
The charging efficiency of the current AGV trolley wireless charging products is comparable to that of the contact charging system. Non-contact wear and a high degree of intelligence make it ideal for online charging.
How to extend the battery life of AGV & AMR
Reasons for abnormal damage and charging concept
Overcharging can cause damage to the battery’s positive plate. Generally, the positive plate fracture is at the upper root. Under the condition of overcharge, the atomic oxygen corrosion on the surface of the plate directly causes the lower connection strength of the plate to be unabated. This also shows that it is caused by the uneven distribution of excessive charging current.
There is no electricity on the charged plate, which is also a concept that will be misunderstood by everyone. If the battery plate after charging is energized, it will be short-circuited by the acid electrolyte, so there is no electricity inside the battery, and there is only chemical energy.
Electrical energy is converted into chemical energy during charging. If the form of this energy is not completed in the conversion battery, it will be overcharged, and the flow of battery power will accelerate the damage of the battery. Therefore, do not think that charging the battery, there must be electricity in the battery.
Avoid hardware requirements for overcharging
The charger should have a three-level charging function
The battery current of the AGV trolley should conform to the current receiving frequency of the tracking static battery. Its basic procedure is automatic conversion in three stages, high current constant current, gassing voltage, constant voltage, and small current constant current.
should be installed on the motor car
If the ammeter is not installed on the battery locomotive, the user actually does not know the capacity consumed by the locomotive to complete the task, so it cannot be performed according to the actual state of the battery during the charging process. Users can only use overcharge to protect battery capacity.
The data safety limit can be determined by detecting the data according to the actual time of the chronometer. Under deep discharge conditions, the plate expansion and contraction of the battery will be large, and the physical structure of the plate is also easily damaged. The lower limit of the battery should be kept at 20% of the capacity. When the battery is used properly, the battery capacity cannot be discharged. The conditions of use of different mines are also different, and the slope, the specified number of tractions, and the number of times of operation are different. Therefore, the safety margins of the mines are also very different.
A reasonable safe use limit is that the capacity of 20% plus traction discharge is equal to the battery use standard of the battery, and the battery with Cmin lower than the capacity Cmin cannot be boarded. The important task of the battery team is to pick out the battery with a capacity lower than Cmin and replace it with a qualified product.
Corrosion protection should be applied to the positive electrode of the battery
When the new battery is used, a positive electrode protectant should be added, which can effectively reduce the amount of oxygen evolution during charging, thereby reducing the corrosion of the positive grid by charging. According to the Kunshan Ye Mao electromechanical test, the battery life of the positive electrode protector can be increased by 50%.